The OntoTrans project responds to the need of industry to respond to manufacturing challenges more efficiently by accessing the relevant information and utilising materials modelling more effectively. In particular, there is a need to strengthen the use of translation as a router supporting end users to get to relevant data and models.
What is Translation?
In the context of OntoTrans, translation is the process of translating industrial problems into questions to be solved using modelling and simulations tools for, e.g., creating industrial innovation.
Translators pick up industrial challenges, transform them to modelling workflows, and guide manufacturers in execution and interpretation of modelling results.
What is a Translator?
Translator is not an individual person but is a role which is usually best fulfilled by a team of people with skills required for the efficient execution of the Translation process. The Translator role may differ in terms of required skills, depending on the specific case/client.
Translators work on the interface between business and R&D during all stages of the development (design, testing, up-scaling, market introduction) and should focus on the industrial problem. Before any possible modelling workflows or simulation cases are proposed, a full understanding of the problem and its industrial context is necessary. Translators support the implementation and utilization of modelling and simulation by enhancing the skills of the industrial operators. This is best accomplished by adapted training efforts.
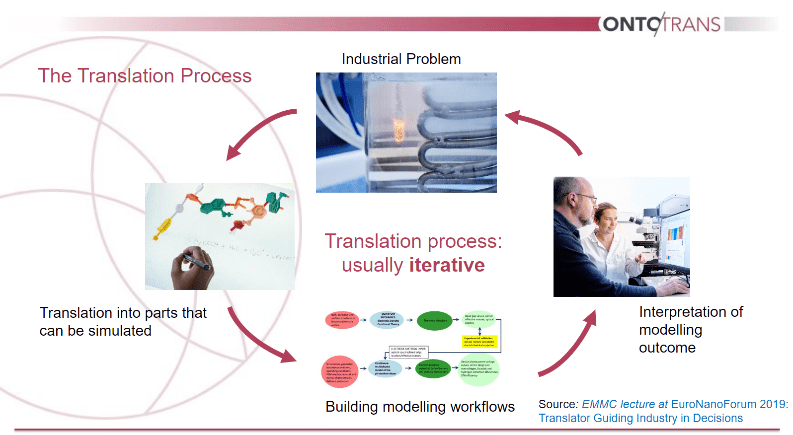
OntoTrans provides a general-purpose ontology-based Open Translation Environment (OTE) able to support the development of dedicated Apps delivering a smart guidance for materials producers and product manufacturers (including associated Translators) through the whole steps of the translation process (see Figure), by:
1. representing manufacturing process challenges in a standard ontological form as technical and business User Cases (UC)
2. connecting user cases with existing appropriate information sources i.e. available data and materials modelling solutions
3. recommending consistent materials modelling workflow options
4. supporting simulation and validation activities
5. providing semantic results interpretation to facilitate sharing and re-use of user cases and results
with the final aim to improve decision making processes in a smart integration of Open Simulation Platforms (OSP), data-driven models, materials databases, exploratory and recommendation system and ontology driven database.
Information on translation refers to the EMMC Translation Guide