
The OntoTrans Consortium wishes you Happy Holidays and a joyful New Year! Thank you for following our project‘s progress, attending our events, following our social media accounts and reading our newsletters this year. We are looking forward to another year of engaging workshops, lively discussions, innovative research, new ideas and European collaboration.

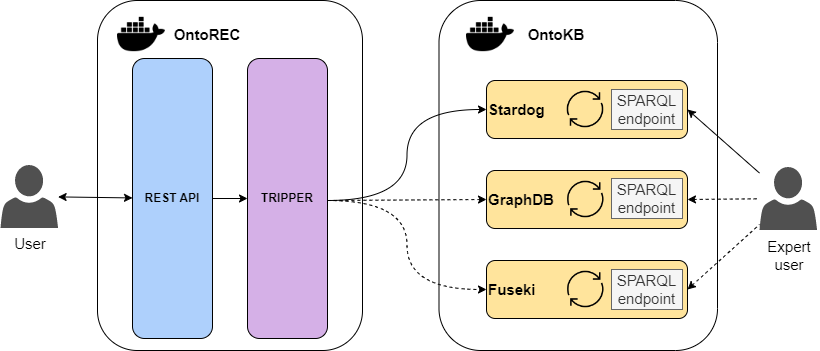
The OntoTrans Core Components are the principal elements responsible for addressing and favouring the semantic interoperability in the OntoTrans system thanks to the ontologies management, querying, and recommending capabilities. They consist of a couple of software products that come in a containerized fashion facilitating the deployment on heterogeneous platforms: OntoKB and OntoREC.
More in detail, OntoKB is the knowledge base for the OntoTrans system and relies on an underlying triplestore able to provide persistent storage, management and querying of ontological concepts that manufacturing companies can provide. However, what distinguish a triplestore from a database is a reasoning engine capable to infer new concepts starting from the present ones. There exist several solutions to choose among, but the current implementation leverage Stardog as the main triplestore supported. Given its ontologic-related nature, OntoKB does not contain raw and proprietary data since it is not designed to serve as a traditional relational database. In fact, one of the principal purposes of OntoKB is to store all the metadata and the mappings between ontological concepts and data models, hence, favouring semantic interoperability among different domains.
On the other hand, OntoREC is a python REST-based proxy designed to provide an abstraction layer for the functionalities of OntoKB as well as to act as a controlled access point. Currently, the main supported features regard the implementations of the CRUD operations (Create, Read, Update, and Delete) for the management of ontologies, namespaces, and databases (intended as independent workspaces) and the possibility to query the knowledge base by submitting custom SPARQL queries. By default, the usage of OntoREC is not mandatory; there is also the possibility, for an expert user, to use directly OntoKB at the cost of losing the abstraction layer provided by OntoREC. Furthermore, in a future release, OntoREC may embed some optimizations to improve and speed-up general performances (e.g., caching past queries and results).
Since the current implementation of OntoREC makes use of some non-standard APIs to interact with OntoKB (i.e., Stardog native APIs), an eventual change of triplestore technology (e.g., leveraging GraphDB instead of Stardog) would require a non-negligible effort to map the functionalities of OntoREC on a different triplestore.
Given these issues, our current development effort is aimed in making OntoREC independent of the specific triplestore in OntoKB by adding a layer in charge to handle all the triplestore-specific details. Such independence is achieved through the Tripper, an extensible python-based tool provided by SINTEF (a partner involved in OntoTrans) to interface several triplestores easily. The Tripper integration within OntoREC will allow to overcome the functional differences present in the various solutions, concerning the current features supported by the tool. With these further developments, OntoREC will fulfil the required needs by exposing a uniform interface that will make the underlying technology choice transparent from both a functional and location perspectives.
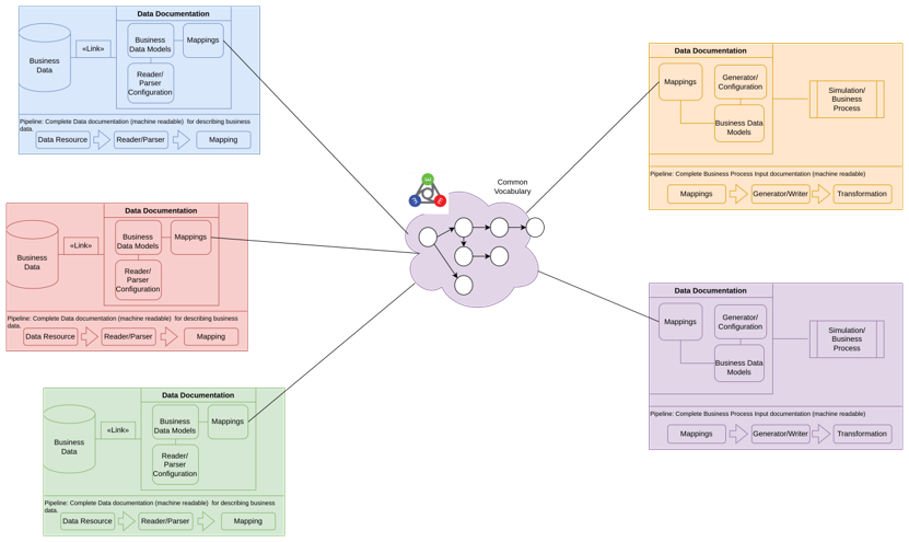
Data pipelines are used to describe and automate data flow between data sources and data consumers. The elements of the pipeline documents how to access data, how to extract information, how to limit the data and how to understand the data (in terms of ontological concepts). On the consumer side, the pipelines are used to define what data is needed (as input) to a transformation, visualization or for storage. Each data source or transformation can be documented using a "partial pipeline". Dynamic construction of a complete pipeline can be performed when a data-producer (source) is connected to a data consumer (target). This allows for a flexible "mix-and-match" configuration of workflows while still ensuring consistent, complete and accurate data exchange.
Gerhard Goldbeck (European Materials Modelling Council Executive Secretary and OntoTrans Technical Manager) presented the EMMC led Working Group 1 'Materials Digitalisation' during the 'Discovering AMI2030 - The European Advanced Materials Initiative' event on December 16, 2022. In the presentation he talks about materials digitalisation objectives, creating a common materials data space and digitally integrating and iterating data and knowledge activities throughout the life cycle. Working Group 1 will contribute to finalising the AMI2030 Roadmap, detailing the priorities in data-driven development of advanced materials and materials data management.
The goal of the Advanced Materials 2030 Initiative and the vision of the Materials 2030 Manifesto is to build a strong European Materials ecosystem driving the green and digital transition as well as sustainable inclusive European society through a systemic collaboration of upstream developers, downstream users and citizens and all stakeholders in between. This will accelerate the development of sustainable advanced materials and create a new vision of Advanced Materials for Europe to remain competitive.
You can watch the recording of the whole 'Discovering AMI2030' event here or skip directly to minute 50 to just watch the presentation of Working Group 1.
To learn more about the European Advanced Materials 2030 Initiative you can visit the official webiste.

OntoTrans together with its Project Group focuses on improving industrial data quality, interoperability and traceability through the adoption of ontologies and standards. The project Group includes OntoTrans’ related projects NanoMECommons, OntoCommons, OpenModel, VIPCOAT, OYSTER and ReaxPro.
With the support of the specialised company Trust-IT Services, OntoTrans was able to identify objectives of the Project Group and to start dissemination activities under the cluster it leads. Under the umbrella of the HRB and together with the Project Group, OntoTrans coordinated the OntoTrans Collaboration Session in the First OntoTrans Open Workshop to foster collaboration and support building an interconnected ecosystem for industrial partners.
To complete the activities of the Horizon Results Booster a joint factsheet and a joint video were created. The fact sheet and joint video introduce the Project Group’s common objective: improving manufacturing and materials data quality, interoperability and traceability.

The OntoTrans Consortium had the opportunity to meet for the first time in Brussels for the M30 Consortium Meeting. The hybrid meeting was hosted by our project partner Procter and Gamble's InQbet Accelerator. During the meeting the project's progress, status, future tasks and new ideas were discussed. The Consortium had an enjoyable and productive time, thanks to the superb organisation of the meeting by our partners from P&G and the expertise and outstanding dedication of each partner contributing to the project's success.

Our colleagues and members of the OntoTrans Consortium Francesca Lønstad Bleken, Jesper Friis and Inga Gudem Ringdalen from SINTEF (Norway) publishesd an interesting article about interoperability and ontologies in the Norwegian Newspaper 'Dagsavisen'. The article offers a compensive overview of the linguistic logic with its origins in ancient philosophy and how it helps us now in the search for green future materials.
To read the article in English or Norwegian visit Dagsavisen's website.
The OntoTrans Technical Manager Gerhard Goldbeck (Goldbeck Consulting, UK) represented OntoTrans at the 1st International Symposium for Materials R&D Data of Nano Korea 2022 organised by the National Center for Materials Research Data of Korea. The hybrid symposium highlights global activities for materials R&D data that can be utilised for more efficient materials design and materials process optimization. Gerhard Goldbeck's presentation deals with the question of how to improve interoperability in a complex field of many perspectives.
To view the presentation visit the OntoTrans website.

M01 Kick Off Meeting / Online / April 21-22 & 24, 2020
M06 Consortium Meeting / Online / October 07-08, 2020
M12 Consortium Meeting / Online / May 05-07, 2021
M18 Consortium Meeting / Online / September 09-10, 2021
M24 Consortium Meeting / Online / April 6-7, 2022
M30 Consortium Meeting / Brussels / October 17-18, 2022
Technische Universität Wien, Austria
Goldbeck Consulting, United Kingdom
Alma Mater Studiorum - Università di Bologna, Italy
Fraunhofer, Germany
SINTEF, Norway
Helmholtz-Zentrum Hereon, Germany
CMCL Innovations, United Kingdom
Datastories, Belgium
ArcelorMittal, Spain
Composites Evolution, United Kingdom
Procter & Gamble, Belgium
